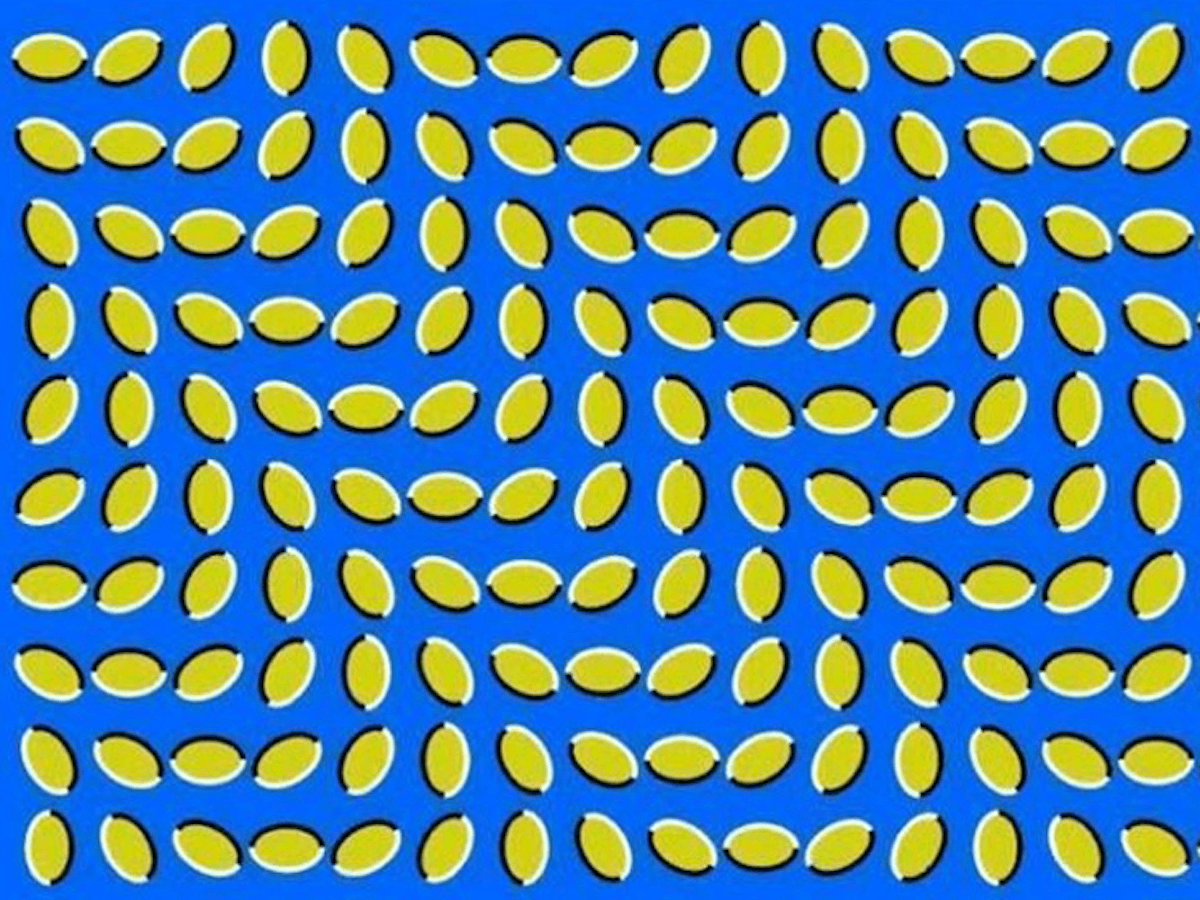
The sort of thing I love is how our brains handle visual information. They process 11 million bits every second, but we only consciously notice about 40 bits. This remarkable difference helps explain why optical illusions can fool our minds so effectively and make us doubt what we see.
We’ve put together 10 fascinating visual illusions that will make you question your perception of reality. These examples show how our visual processing isn’t as dependable as we might assume. Classic psychological illusions have mystified people for generations, while modern perceptual illusions take advantage of our brain’s pattern-recognition systems. These remarkable phenomena connect the worlds of neuroscience, psychology, and art seamlessly.

The Science Behind Visual Deception
The human brain’s creation of reality offers a captivating study in visual deception. Research shows that our perceived reality differs from an exact representation of the world .
How Your Brain Processes Visual Information
The visual system works through a complex sequence starting at our eyes. Light moves through the cornea, passes the pupil and lens, and reaches the retina where photoreceptors transform it into neural signals. These signals flow through two main parallel pathways: the optic and pupillary reflex pathways.
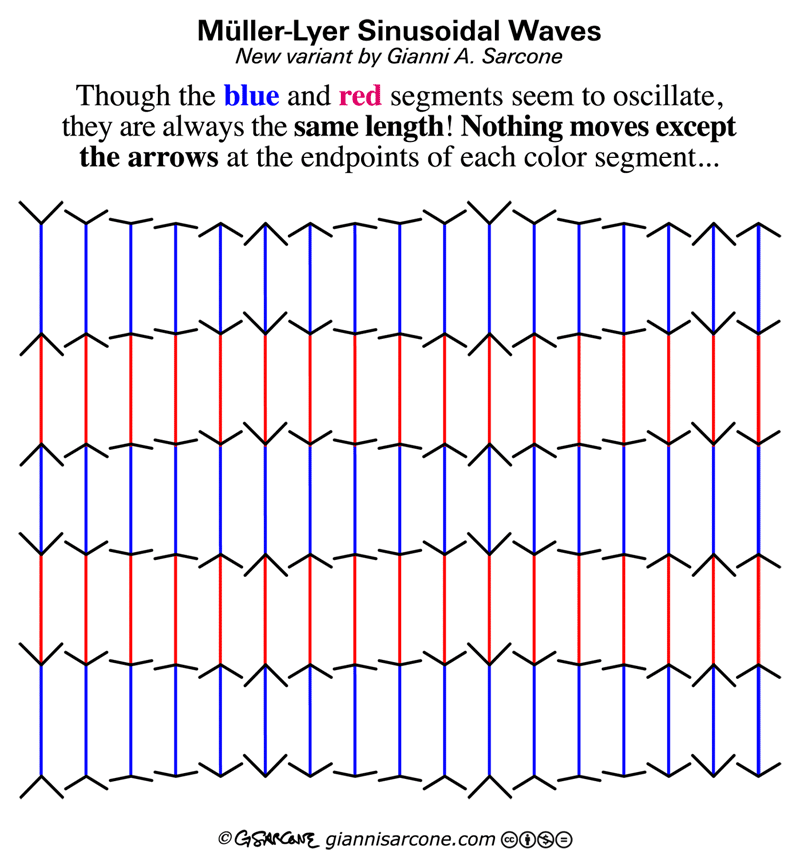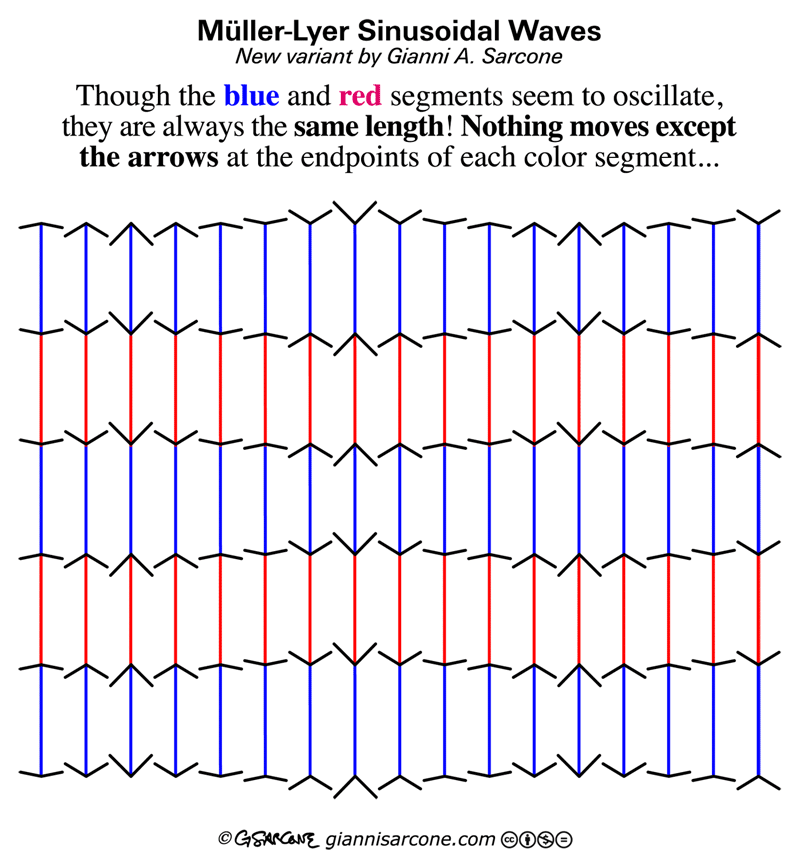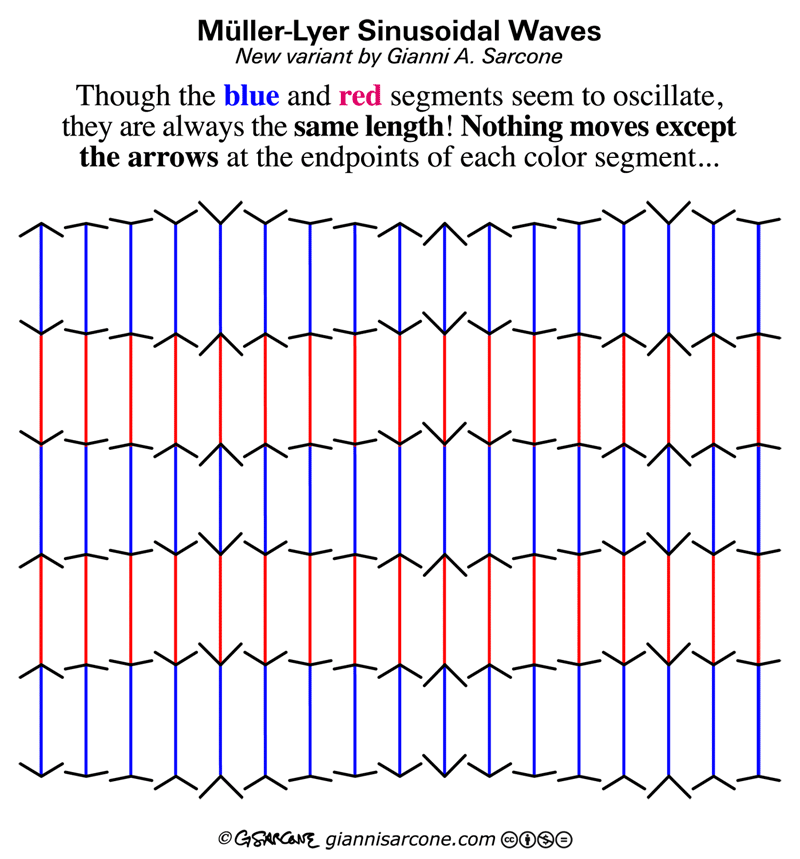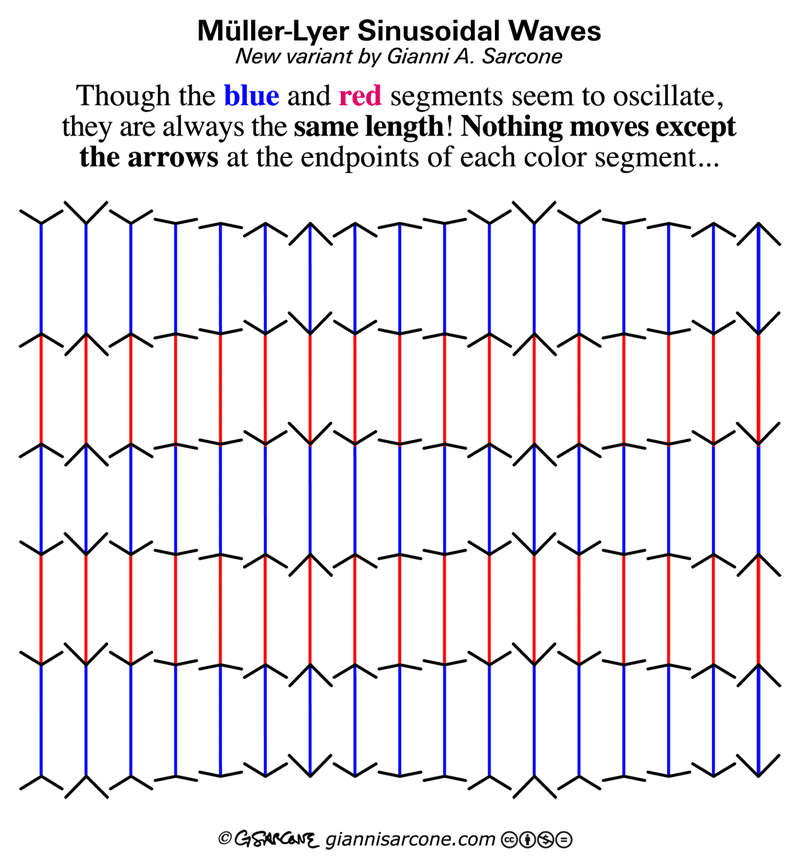
The process happens in three key stages:
- Pre-attentive Processing: Billions of neurons extract simple features
- Pattern Formation: Visual field divides into regions and simple patterns
- Active Interpretation: The brain makes sense of what we see
Why We Fall for Optical Illusions
Our brain actively builds reality instead of just receiving it passively. Scientists have found that visual processing takes 50-100 milliseconds, which forces our brain to predict and fill gaps. This predictive nature creates three distinct types of optical illusions:
- Literal Illusions: Created by multiple overlapping images
- Physiological Illusions: Cause us to see non-existent elements
- Cognitive Illusions: Challenge our learned assumptions about the world.
The Role of Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition shapes our visual information processing fundamentally. The visual cortex processes initial data, yet research reveals that 20% of neuronal activity in the visual cortex comes from feedback mechanisms rather than direct visual input. This explains our brain’s power to “see” shapes that don’t exist, like in famous optical illusions.
The frontal lobes serve a vital part by making decisions about visual input based on past experiences and expectations. People interpret the same visual illusion differently because their brains complete ambiguous information using familiar experiences.
These mechanisms explain why optical illusions work so well. They don’t just fool our eyes – they take advantage of our brain’s systems to understand the world. Visual illusions showcase our brain’s remarkable power to construct reality, even when that construction contradicts the physical world.
Classic Illusions That Still Baffle
Three remarkable optical illusions have challenged our understanding of visual processing through the ages. These enduring mysteries engage scientists and viewers alike, generation after generation.
The Impossible Triangle Mystery
The Penrose triangle stands out as a masterpiece of illusion. Swedish artist Oscar Reutersvärd created it in 1934. Mathematician Roger Penrose later made it famous, calling it “impossibility in its purest form”. Our brain tries to make sense of it as a three-dimensional object, yet it cannot exist in our three-dimensional space.
Key features of the Impossible Triangle:
- Appears normal at first glance
- Creates cognitive dissonance upon closer inspection
- Can only exist as a two-dimensional representation
- Can be physically constructed to work from one specific viewing angle
Rotating Snakes Phenomenon
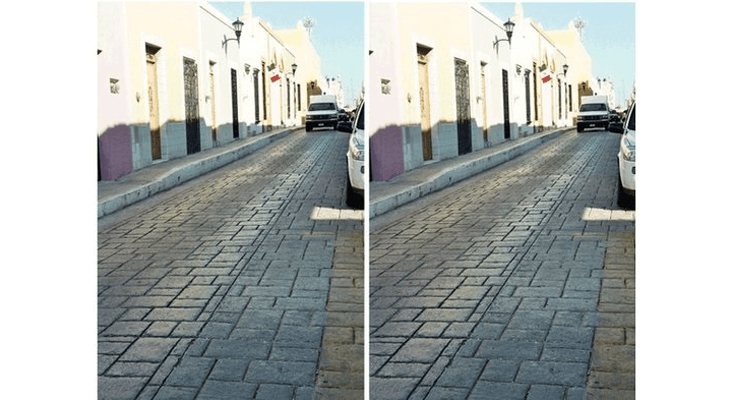

Akiyoshi Kitaoka’s Rotating Snakes illusion from 2003 shows how static images can appear to move. The illusion works because of three vital aspects of our visual system:
- Rapid neural firing when images change, followed by quick deceleration
- Image processing at various spatial scales
- Detection of large-scale global motions
The sort of thing I love about this illusion is how it stops working when you stare at one spot, yet continues when your eyes move around the image. This shows how our eye movements create the perception of motion in static patterns.
The Famous Café Wall Effect
Scientists found this illusion on a café wall in Bristol. The Café Wall creates an appearance of slanted lines where only parallel ones exist. Three elements make this illusion work:
- Alternating dark and light tiles
- Visible mortar lines between tiles
- Half-tile offset in adjacent rows
The illusion’s power comes from our neurons’ interaction in the brain. They dim and brighten different parts of the gray lines based on tile positioning. Research points to interactions between visual cortex neurons that code for orientation, though we don’t fully understand the exact mechanism yet.
Modern Digital Illusions
The digital age has brought a complete shift in how we create, share, and experience perception optical illusions. Technology meets visual deception to unlock new ways of tricking our minds.
Social Media’s Viral Optical Illusions
Social media platforms have seen a surge in optical illusions, with certain images catching everyone’s attention worldwide. Here are some viral examples:
- The “Dress” phenomenon sparked worldwide debate about color perception
- The “Cat with Human Arm” illusion made people see impossible anatomy
- The “Invisible Woman on Mountain” showed perfect camouflage
- The “IKEA or Ocean View” confusion played with our view
AI-Generated Visual Tricks
Artificial intelligence now creates its own perception optical illusions. The technology has grown substantially, and AI systems can generate complex visual deceptions that weren’t possible before. These systems mix existing technologies in new ways to create images with hidden encoded meanings while keeping the original subject intact.
AI-generated illusions stand out because they can:
- Create multi-modal experiences that mix visuals, audio, and text
- Generate highly targeted influence based on personal data
- Produce realistic effects that convince our bodies of physical experiences
Interactive Digital Illusions
Digital illusions have made remarkable progress in our everyday experiences. Immersive technologies have changed how we interact with visual deceptions. Computer-generated imagery (CGI) plays a crucial role in creating these experiences, and modern visual media leaves virtually no pixel untouched.
These innovations shine in several key areas:
- Entertainment: Creating smooth visual effects in movies and games
- Healthcare: Supporting medical diagnostics and training
- Education: Enhancing learning through interactive visualizations
- Marketing: Developing engaging advertising experiences
Modern digital illusions stand out because they adapt live to user interaction. This creates tailored experiences that weren’t possible before. These technologies don’t just fool our eyes – they open new ways to perceive and interact with visual information.
Real-World Applications
The science and history of perception optical illusions fascinate many. Yet their most exciting aspect might be how they’re reshaping our world in amazing ways. These visual tricks now power everything from towering skyscrapers to medical breakthroughs.
Architecture and Design
Perception optical illusions turn ordinary structures into extraordinary experiences in modern architecture. The Greeks started these techniques first. They made subtle adjustments to create perfectly proportioned structures Modern architects now build on this legacy. Their designs challenge how we see and understand space.
Here are some amazing examples:
- Poland’s Baltyk Building seems to defy gravity from different angles
- Disney’s Sleeping Beauty Castle looks bigger through forced perspective, with brick sizes getting smaller as the castle rises
- The Hartford Steam Boiler building’s mirror-like surface creates endless reflections
Marketing and Advertising
Visual illusions have found their way into clever ad campaigns. Coca-Cola showed this brilliantly in 2015. They used optical illusions to showcase their plant-based bottle initiative. Honda took things further with their CR-V commercial. They created all effects right on camera without any digital tricks.
These campaigns work so well because they grab people’s attention. Adding visual content to marketing can boost engagement rates 650% more than text-only posts. Companies that stick to consistent visual branding have seen their sales jump by 33%.
Medical Diagnostics
Understanding perception optical illusions helps doctors make better diagnoses. Radiologists have learned to use these visual tricks to their advantage. While some illusions can lead to mistakes in reading anatomical structures, others help spot abnormalities better.
The benefits show up in several ways:
- Brightness and contrast illusions make structures clearer on medical images
- Pattern recognition helps identify specific conditions
- Knowledge of perceptual biases cuts down the roughly 40 million yearly errors in radiological studies
Doctors now use certain illusions as diagnostic tools. The “winking owl sign” helps them spot spine cancer, while the “snowman sign” tells the difference between pituitary macroadenomas and meningiomas.

Testing Your Perception
Let’s test our visual processing abilities now that we understand how perception optical illusions work. Our collaboration with experts has led us to find fascinating ways to measure and improve how we process visual information.
Interactive Challenges
Testing how susceptible we are to visual illusions helps us learn about our brain’s information processing. The Ben-Gurion University Test for Perceptual Illusions (BTPI) stands out as a standardized tool that measures individual differences in perception. This online battery lets us explore our responses to three prominent illusions:
- The Ebbinghaus Illusion
- The Ponzo Illusion
- The Height-Width Illusion
These tests show us how our brains create shortcuts in visual processing. They help us understand why reality sometimes looks different from what it is and why we make irrational decisions.
Measuring Your Susceptibility
Measuring how visual illusions affect us goes beyond just identifying what we see – it helps us understand our visual processing mechanism. The BTPI looks at two significant aspects:
- The Point of Subjective Equality (PSE): This shows how much each illusion affects us
- The Just Noticeable Difference (JND): This indicates how well we detect size differences
Test-retest results for illusion magnitude showed high reliability. This tells us that our susceptibility to specific illusions stays mostly constant over time.
Training Your Brain
We have found several ways to improve our perceptual abilities. Studies show that regular practice with visual challenges can boost cognitive abilities and help prevent cognitive decline. Here are some training approaches that work:
- Pattern Recognition Exercises: Simple sorting and matching activities strengthen visual discrimination
- Visual Attention Training: Specialized games help filter out unnecessary details
- Sequential Memory Development: Remembering objects in specific orders improves visual processing
- Spatial Relationship Enhancement: Activities that build understanding of how objects relate to each other.
Our tests show these exercises give immediate feedback about reality. This helps people develop more accurate perceptions about themselves and their surroundings.
These training methods fit naturally into daily activities. Simple tasks like organizing drawers or matching socks become valuable perceptual training exercises.
Better understanding of how illusions affect us and active work on our perceptual abilities helps us move through both natural and digital environments more effectively. Success comes from consistent practice and awareness of our brain’s visual processing methods.
Conclusion
The human brain’s visual processing capabilities shine through fascinating perception optical illusions. These captivating phenomena show how our brains build reality instead of just receiving it. The Impossible Triangle and similar classic illusions challenge what we know, while digital technology creates new ways to deceive our eyes.
These illusions serve practical purposes beyond simple entertainment. Talented architects use them to design impressive spaces. Marketing teams create campaigns that stick in people’s minds. Medical professionals even improve their diagnostic skills. These applications demonstrate how visual perception knowledge shapes everyday life.
Visual challenges and brain training exercises are a great way to get tools that boost personal development. Your cognitive abilities grow stronger when you practice with perception tests regularly. This understanding becomes crucial as you direct yourself through a world filled with natural and artificial illusions.
Optical illusion science proves that reality often differs from our perceptions. Visual puzzles give us glimpses into our mind’s complex operations. Each encounter helps us learn about how our brains decode the world we see.